Trust is the foundation of needs-focused leadership.
It develops gradually through authenticity, transparency, reliability, and consistent alignment between words and actions — and once established, it reinforces psychological safety, openness, and collaboration.
Because trust is inherently fragile, even minor breaches of integrity can erode it quickly. Sustaining trust therefore requires continuous, intentional action.
Findings from both the qualitative interviews and the literature review consistently highlighted the tight connection between trust and psychological safety.
In MOVE, they are foundational principles — embedded in practices like emotional frontloading, conflict mediation, and competencies such as:
Facilitating Open Dialogue & Feedback
Attentive & Empathetic Listening
Service-Oriented Leadership
Visionary & Growth-Oriented Leadership
Trust serves as the “glue” that binds the human-centered behaviors in the Process Model with the proactive leadership roles in the Competency Model.
Trust and Psychological Safety
Developing the MOVE Trust Model
The MOVE Trust Model was built by:
Extracting trust-related statements from interview transcripts
Clustering them into thematic categories
Validating these categories against established trust research
Refining the model to focus on active input factors — the attitudes and behaviors leaders can control — rather than passive outcomes
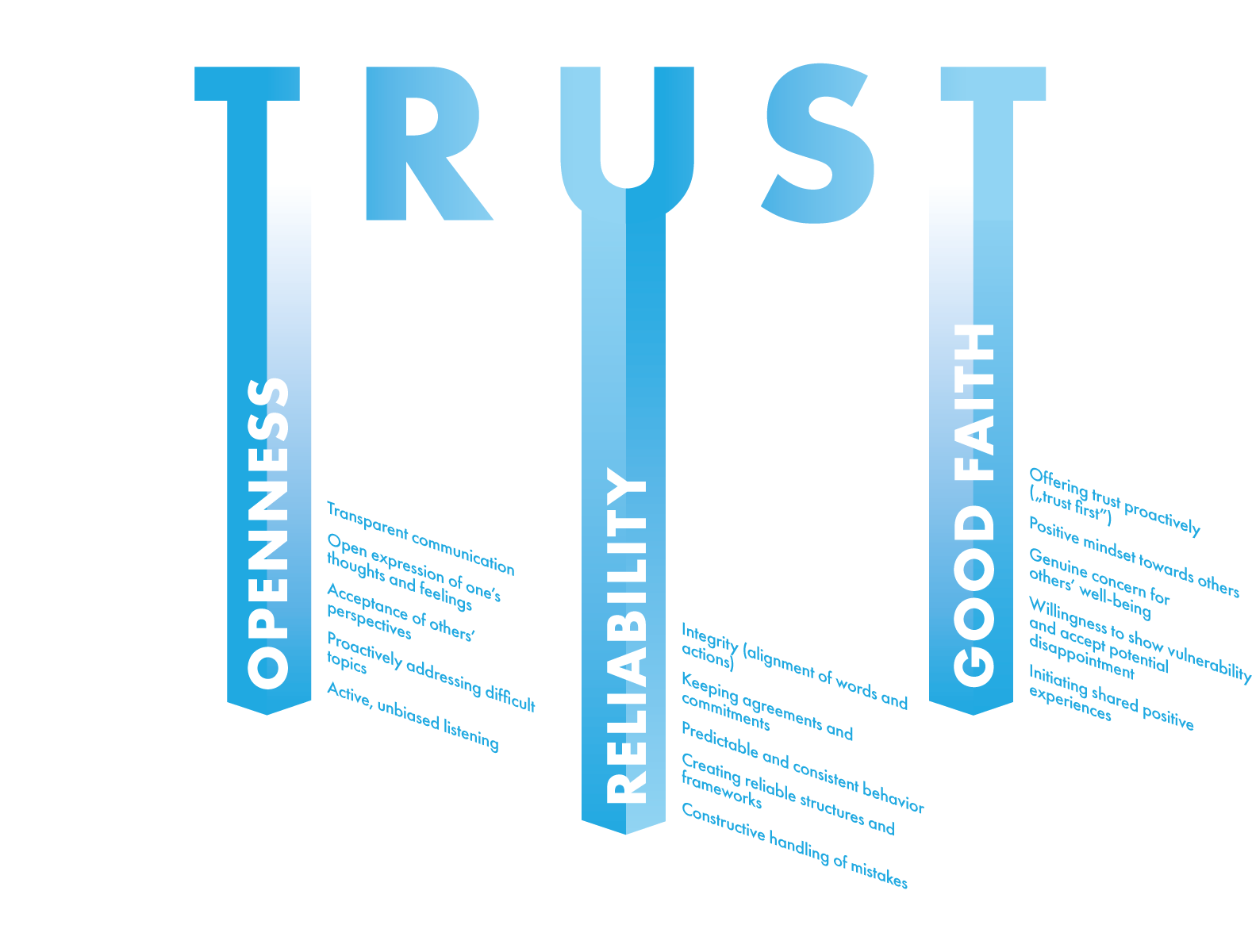
The result is a practical, actionable trust framework with three interdependent components.
The MOVE Trust Tripod
The MOVE Trust Tripod defines three interconnected behaviors—openness, reliability, and good faith—that, when practiced consistently, create the foundation for psychological safety, collaboration, and lasting trust in project teams.
1. Promoting Openness in Communication
Encourage transparency and directness, even on difficult topics
Listen without judgment and invite differing perspectives
Share reasoning behind decisions to build understanding and reduce uncertainty
Model emotional openness to foster authenticity within the team
2. Ensuring Reliability and Integrity
Keep commitments and follow through consistently
Demonstrate structural and behavioral reliability
Address mistakes constructively and take responsibility for errors
Align actions with stated values to maintain credibility
3. Demonstrating Good Faith
Offer trust proactively rather than waiting for others to “earn” it
Maintain a positive, non-cynical mindset toward colleagues
Show genuine care for team members’ well-being and success
Initiate shared experiences that strengthen relational bonds